What Does Merkel Cell Carcinoma Look Like?
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: May 2017. | Last updated: March 2021
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) develops when Merkel cells in the skin begin to grow out of control. Merkel cells are the cells in the epidermis, the top layer of skin. Merkel cells contribute to the sense of touch.
The typical appearance of MCC is described below. It can be hard to identify a lesion correctly on your own. MCC is so rare that even doctors have a hard time identifying it by sight.1 If you notice changes in your skin, discuss them with your primary care provider or dermatologist.
Where does Merkel cell carcinoma develop?
MCC tumors are commonly found on body parts with frequent sun exposure. The most common locations are the face, the shoulders, and upper arms.2 Interestingly, about 15% appear on the hip or legs, and 11% appear on the chest and back.2Less common locations are the scalp, neck, ear, eye lid, and lip.
MCC is more likely to develop on the left side of the body than the right side. This happens because the left side of your body gets more sun exposure while driving than the right side.3
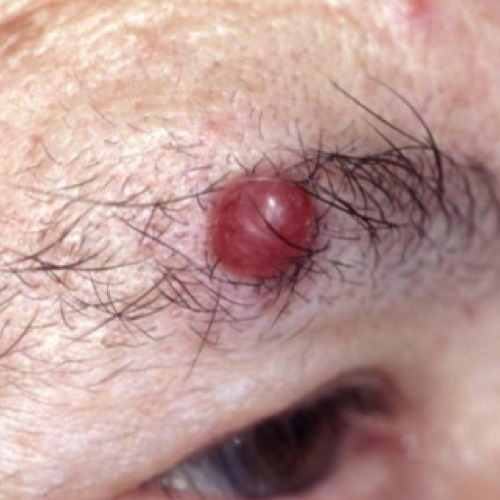
What are the symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma
MCC usually is a painless red or purplish dome-shaped lump.4 Sometimes, the lesion is pink, blue, or the color of normal skin. The tumor usually grows quickly. It may feel firm and look shiny. You may see blood vessels. It may open up and form a sore. MCC can also be a rough, hard patch on the skin.5
What other symptoms of Merkel cell carcinoma might I have?
MCC is aggressive.4 In one-third of patients, MCC has spread to the lymph nodes by the time it is diagnosed.6 Your lymph nodes may feel swollen, hard, or enlarged.
What else could this be?
MCC is rare and does not have distinctive features.1 Many times, your doctor does not suspect MCC. MCC is only identified by examining the skin biopsy.1
MCC may be confused for lesions with a similar appearance, such as:
- Bug bite
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Cyst
- Sty
- Wart