Targeted Therapies
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: May 2025 | Last updated: May 2025
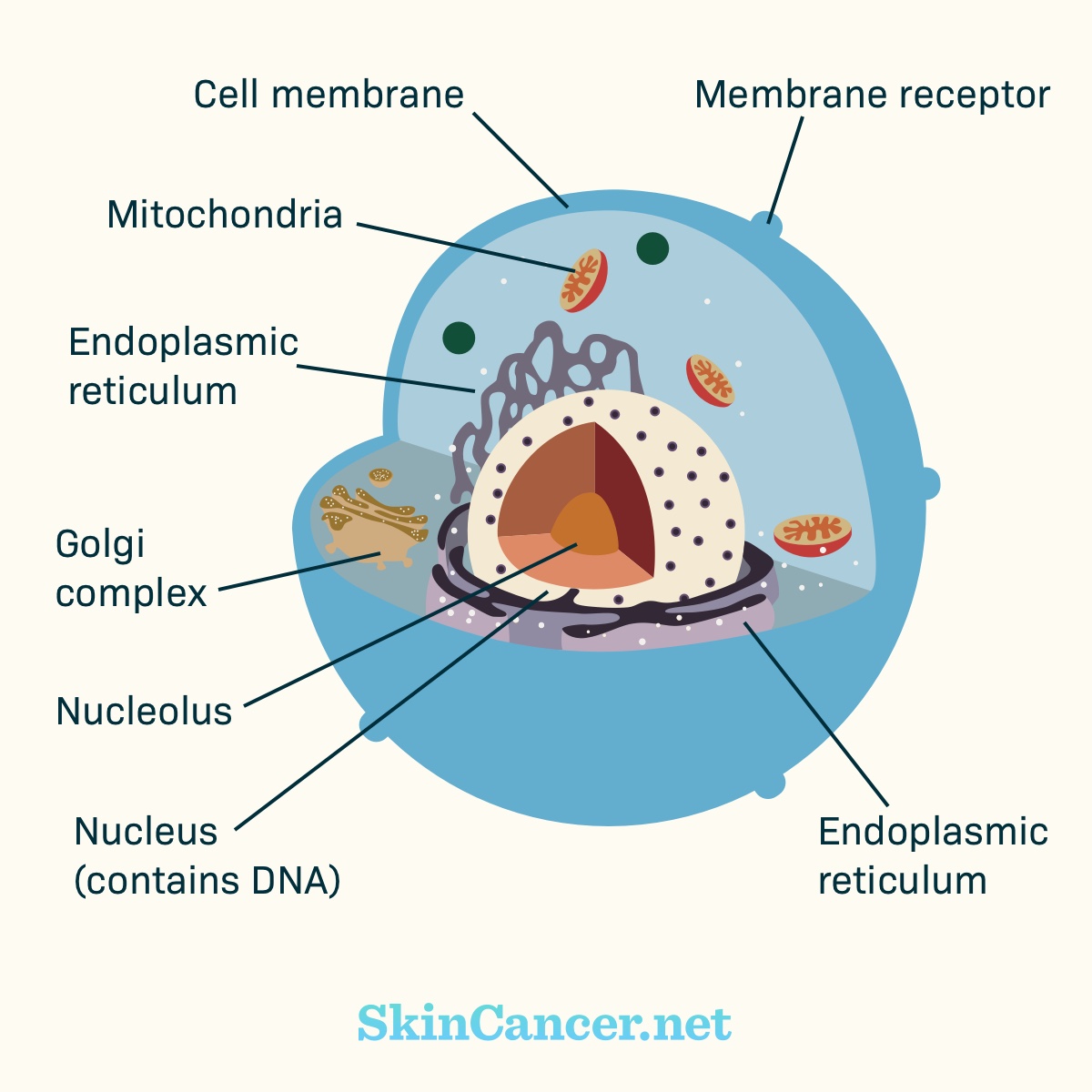
Cancer cells are different from normal cells. Many cancer cells have mutations that cause them to grow and survive when normal cells would not.
Cancer develops when there are harmful changes in DNA. These harmful changes are called mutations. Targeted therapies aim at the features that make cancer cells different. They offer a unique treatment option for certain skin cancers.1
Figure 1. Cell structure
How does normal cell signaling work?
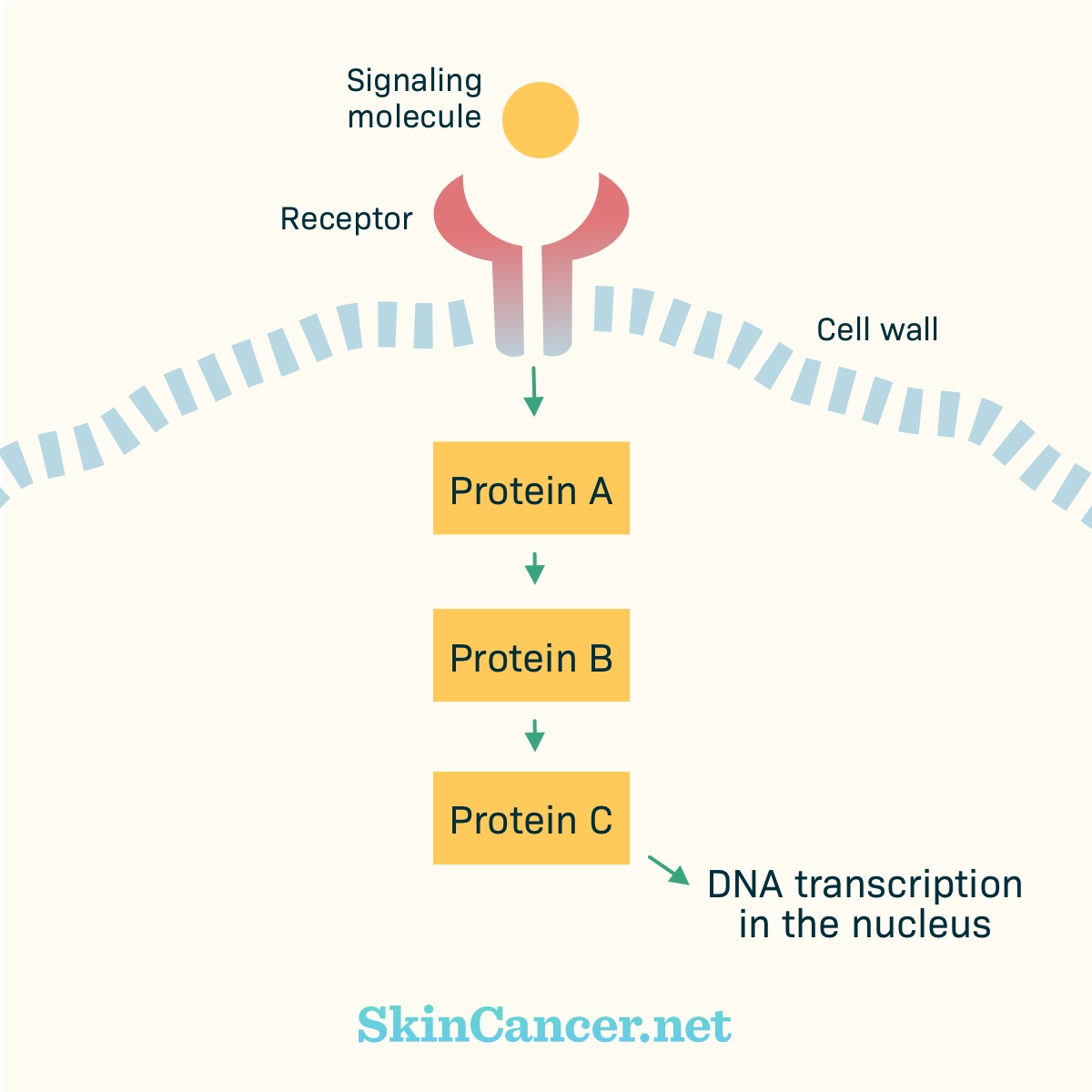
There are receptors within the cell membrane. Part of the receptor may stick out of the cell (“extracellular domain”). Part of the receptor may stick into the cell (“intracellular domain”).
Receptors receive chemical signals from outside the cell. Examples of chemical signals are hormones, growth factors, or cytokines. The chemical signal binds with (plugs into) the receptor. Binding activates (turns on) the receptor. The activated receptor changes within the cell. Proteins may move toward the receptor and activate other proteins.
These proteins pass signals from one to the other, like a game of telephone. Eventually, the signal gets to the nucleus. In the nucleus, the instructions for building a protein are copied from the DNA. Other parts of the cell assemble the protein.
In normal cells, there are “on” and “off” switches for these chains of events. A pathway only becomes active as needed.
Cancer develops when there are harmful changes in DNA. These harmful changes are called mutations. For example, a mutation can lead to a receptor that stays active all the time, instead of turning “on” and “off” as appropriate.
Figure 2. Basic cell signaling
How is targeted therapy used to treat skin cancer?
Targeted therapies are available to treat some types of skin cancers. Specifically, targeted therapies treat:1-3
- Advanced melanoma with BRAF mutation
- Advanced melanoma with c-KIT mutation
- Advanced basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
What targeted therapies treat advanced melanoma with BRAF mutation?
Targeted therapies have improved outcomes for people with advanced melanoma. Advanced melanoma may generally be defined as cancer that:1,2
- Has spread to distant parts of the body (metastasized) or
- Cannot be treated with surgery (unresectable)
About half of melanomas have mutations in the gene (instructions) for a protein called BRAF. BRAF is a protein in the MAPK (or ERK) pathway, which is involved in the cell's growth. BRAF mutations can cause cancer cells to grow uncontrollably.1,2
Today, there are several drugs for advanced melanoma with BRAF mutation, including:1,2
- Dabrafenib (Tafinlar®)
- Vemurafenib (Zelboraf®)
- Trametinib (Mekinist®)
- Encorafenib (Braftovi™), which is used in combination with binimetinib (Mektovi®)
- Dabrafenib and trametinib may also be used in combination. In addition to treating advanced melanoma, this combination may also be used as adjuvant (second) treatment for certain forms of melanoma after the melanoma has been surgically removed in people with disease in the lymph nodes.
- Cobimetinib (Cotellic®), which is used in combination with vemurafenib (Zelboraf®)
- Cobimetinib (Cotellic®) and vemurafenib (Zelboraf®) may be used in combination with atezolizumab (Tecentriq®) immunotherapy
These drugs have slightly different uses. The BRAF and MEK inhibitors treat certain forms of melanoma with the BRAF V600E mutation. V600E is the most common type of BRAF mutation in melanoma. Most of these medicines may also be used to treat some forms of melanoma with the BRAF V600K mutation.1,2
Medicines that target BRAF gene mutations in certain forms of melanoma improve response rates, progression-free survival, and overall survival. They have somewhat different side effects.1,2
MEK is a protein that is further along the MAPK pathway. Medications that target MEK include:1,2
- Cobimetinib (Cotellic®)
- Trametinib (Mekinist®)
- Binimetinib (Mektovi®)
Certain MEK inhibitors may be taken by themselves, but when taken this way, MEK inhibitors may not work for some patients. That is why these medicines are often paired with a BRAF inhibitor:1,2
- Tafinlar/Mekinist®
- Zelboraf/Cotellic®
- Braftovi/Mektovi®
What targeted therapies treat advanced melanoma with c-KIT mutation?
Imatinib (Gleevec®) and nilotinib (Tasigna®) may be options for advanced melanoma with c-KIT mutation.2
The c-KIT receptor kick-starts several different signaling pathways. Up to 20 percent of acral or mucosal melanomas have c-KIT mutations. These are types of melanoma that are not related to sun exposure.2
What targeted therapies treat advanced basal cell carcinoma?
Surgery is more effective than targeted therapy for BCC. Therefore, medicine is typically only used when surgery or radiation are no longer options. Two drugs called SMO inhibitors treat certain forms of advanced BCC:3
- Sonidegib (Odomzo®) – treats locally advanced BCC only
- Vismodegib (Erivedge®) – treats metastatic and locally advanced BCC
Both medicines carry a serious risk of birth defects and stillbirth. Other common side effects of these medicines include muscle spasms, hair loss, and taste changes. The label for Odomzo includes a warning about rare but serious muscle injury.3
What are the side effects of targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy for skin cancer, while designed to attack specific cancer cells, can still cause side effects. These side effects vary depending on the particular drug used.4
Common side effects include:4
- Skin problems like rashes, dryness, itching, and increased sensitivity to sunlight
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Changes in blood pressure
- Liver problems
These are not all the possible side effects of targeted therapy drugs. Talk to your doctor about what to expect when taking targeted therapy drugs. You also should call your doctor if you have any changes that concern you when taking targeted therapy drugs.
If you are receiving targeted therapy for skin cancer, it is crucial to maintain open communication with your healthcare team to manage any side effects that may arise.4