Actinic Keratosis
Reviewed by: HU Medical Review Board | Last reviewed: May 2017. | Last updated: August 2022
Actinic keratosis is a precancer, or a skin abnormality that could lead to cancer that forms when cells in the top layer of skin begin to grow abnormally. The most likely location for an this precancer is sun-exposed skin. If you notice one actinic keratosis, it is likely that you have others.1,2
Many actinic keratoses never progress. About one-quarter go away on their own.3 However, up to 10% may progress to squamous cell carcinoma.4 For this reason, your doctor might suggest treating these lesions.
It may also have many different appearances. Common presentations are described below. However, it can be hard to identify what kind of lesion you are seeing. If you notice changes in your skin, discuss them with your primary care provider or dermatologist.
Where does actinic keratosis develop?
More than 80% develop on skin that gets frequent sun exposure.3 The nose, cheeks, and lips are common locations. This can also develop on the ears, temple, forehead, scalp, shoulders, and neck. They may be found on the back of the hands and forearms.3,5
What does actinic keratosis look like?
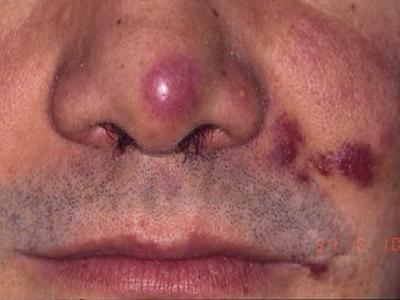
Actinic keratoses range in size from a tiny spot to 1 inch in diameter.5
These lesions appear in many different ways.1,2,5 They are often described as crusty, scaly, or rough. Some people describe the affected area as “feeling like sandpaper.” It may look like a bump, patch, plaque, or horn. The color ranges widely. Normal skin color, red, or pink is common. Some are brown, white, yellow, or silvery.
What are the symptoms of actinic keratosis?
Actinic cheilitis is a type of actinic keratosis that develops on the lower lip.5,6 Symptoms include chapping and cracking. The lesion may appear white or brown. The lip may feel like sandpaper.
Aside from noticing the lesion, you may not feel any symptoms.3 In some cases, it may itch or burn.3 It may be painful to rub the lesion.1
What else could this skin lesion be?
Other conditions that may have a similar appearance as actinic keratosis are:7,8
- Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
- Age spots/Liver spots
- Seborrheic keratoses
- Bowen disease (also called squamous cell carcinoma in situ)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Basal cell carcinoma
- Melanoma